In sheet metal, there are only two processes often used. Fabrication and Forming. The designer at a broad level should know available manufacturing methods keeping in mind the production quantities. For low volume production CAPEX should preferably be avoided. Wherever possible, parts must be designed using general-purpose tooling rather than specialized tools.
1. Small Size Fabricated Parts
Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) vs Volume
Example: High Volume Production
Investment on Forming Tool is justified.
Example: Low Volume Production

Investment in Forming Tool is not justified.
The manufacturing methods for fabrication and forming vary widely depending upon the size and complexity of parts. There is a wide range of machinery from simple manually operated fly presses to totally computerized machines to perform required duties. The designer in consultation with the production specialist should decide on the manufacturing options available to suit the design.
Sheet metal using an established CNC industry may not particularly be good for small parts. It may be expensive. However, in countries like India, there are many micro-scale industries that can cater to such requirements with makeshift tools and equipment. They may be adapted to test prototypes though compromising on tolerances a bit. A manually operated fly press without electric power can surprisingly generate many interesting parts.
 Punched components using fly press. (Image source)
Punched components using fly press. (Image source)
 A cabinet of this kind is easily done on a fly press.
A cabinet of this kind is easily done on a fly press.
2. Large Size fabricated Parts

(Image source)
Large size fabricated parts however are made joining together different parts made by different methods into one part. Welding is more often used in large part fabrication although riveting and screwing are also frequently used. A designer must design the components keeping in mind the joints and the method of joinery. A designer should make provision for jigs and fixtures locations in consultation with production personnel and as to how to handle the part during and post-manufacturing.
3. Small Size Formed Parts

Simple forming operation by fly Press.
(Image source)
Here again, simple forming operations can be achieved on manually operated power presses with makeshift tools. Tool designers can produce low-cost limited-use tools. They are useful to test joinery and to develop prototypes. Medium-sized power presses and CNC tooling can opt for precision production.
4. Medium Size Formed Parts
 Medium capacity Power Press.
Medium capacity Power Press. Design of a cooking stove using formed components on medium capacity press.
Design of a cooking stove using formed components on medium capacity press.5. Large Size Formed Parts
Large formed parts need large machinery and expensive tooling. It is a capital expenditure process and demands high volumes to justify such expenditure. But once properly proven tooling is in place tens of thousands of parts can be produced. The cost of tooling will be amortized over the number of parts produced.

A 2000 Ton press used for an auto body part forming.
(Image source)
6. Other Manufacturing Methods
We have reviewed manufacturing processes in detail in “Chapter 3. Sheet Metal Manufacturing processes”. There are other processes available for the designer to opt for appropriate manufacturing methods. Designers must finally balance between quality, time, and cost.
 Roll Forming.
Roll Forming.

 Hand operated fly Press.
Hand operated fly Press. Bending by Fly Press.
Bending by Fly Press. Medium complex component by fly press.
Medium complex component by fly press. Parts using medium capacity Power Presses.
Parts using medium capacity Power Presses.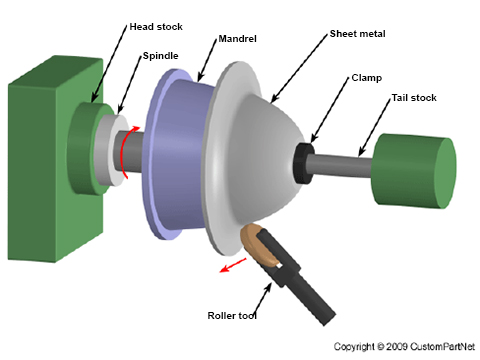 Spin Forming.
Spin Forming.