.
Formal Aspects
Size concerns the physical dimension of an element/object or its representation in terms of the space it occupies.

Size is a relative factor. We can say that an object/representation has a particular size in relation to another. The relationship between different sizes of objects (or representations) or between the dimensions of an object(or its representation) is referred to as ‘proportion’.

The size of the elements in comparison to the world in general is referred to as ‘scale’. Scale is often compared to the size of human body and the space surrounding it. Examples of reference to scale are miniatures, life-size, larger-than-life, monumental scale, etc.
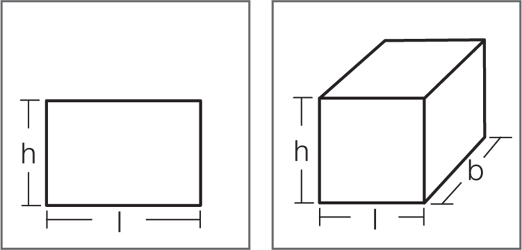
Size can be measured by an object’s (or representation’s) physical dimensions of length and breadth for area or length, breadth and height for its volume.

When seen in perspective, the size of the closer object is represented as larger and farther objects are represented as smaller.
Semantic Aspects
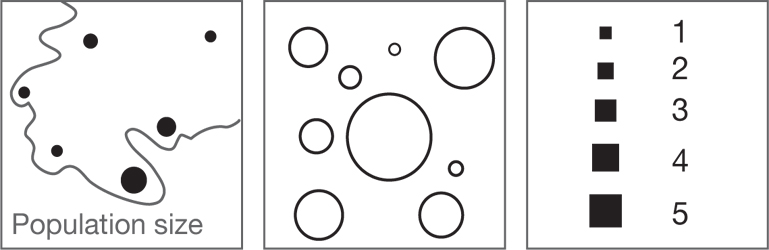
Size variations can be used to denote heirarchy, importance and order.

The size of some features are exaggerated in caricatures. This is to emphasize and bring out the uniqueness of these features.
Practical Aspects

Size indicates the physical dimension of an object or representation.
Size can be altered to denote smallness or bigness of an object or representation in relation to one another.

For practical reasons, drawings and models are done in smaller size to depict objects that are large. This is done by scaling in proportion to the size of the actual objects. For example, architectural drawings can be in ratios of 1:10, 1:20 to the actual size of the building.

