Traditional products:
The project was eventually started investigating on energy sources and finally it shifted to researching the traditional products used in India.
Some of the traditional products used in India, without using any external energy are;
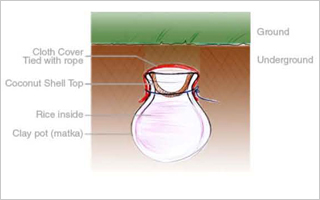
• To store rice in Kerala:
In Kerala, 5 decades ago people were used to store excessive cooked rice in a clay pot covered with coconut shell and they used to bury the pot under the ground, so that the rice remains fresh for many days.
In Kerala, 5 decades ago people were used to store excessive cooked rice in a clay pot covered with coconut shell and they used to bury the pot under the ground, so that the rice remains fresh for many days.

• Matka – Clay pots:
Clay pots or “Matka” (local language of clay pot) is used allover India and different parts of the world for storing drinking water. The water gets cooled due to the seepage of water from the clay pot.
(eg. Matka of clay pots)
Clay pots or “Matka” (local language of clay pot) is used allover India and different parts of the world for storing drinking water. The water gets cooled due to the seepage of water from the clay pot.
(eg. Matka of clay pots)

• Pyaoo:
Pyaoo is a bigger version of Matka which is used to store large quantity of water in the public places and road sides. Pyaoo was made either with clay, animal skin or other different materials.
(eg. Pyaoo with clay)
Pyaoo is a bigger version of Matka which is used to store large quantity of water in the public places and road sides. Pyaoo was made either with clay, animal skin or other different materials.
(eg. Pyaoo with clay)

Pyaoo is very old tradition of drinking water for the common man. The main advantage of this product is the water gets cooled without using any external energy.
(eg. Olden days Pyaoo)
(eg. Olden days Pyaoo)
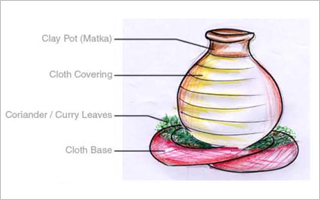
• Clay pot covered with cloth:
Clay pot covered with cloth and also the pot will be rested on a cloth base, vegetable leaves and coriander leaves be kept under this to store as fresh. Because of the property of Clay pot cool water will keep the surrounding area outside of the pot also cools, which makes the leaves cool and fresh.
(eg. Clay pot covered with cloth and leaves kept under)
Clay pot covered with cloth and also the pot will be rested on a cloth base, vegetable leaves and coriander leaves be kept under this to store as fresh. Because of the property of Clay pot cool water will keep the surrounding area outside of the pot also cools, which makes the leaves cool and fresh.
(eg. Clay pot covered with cloth and leaves kept under)
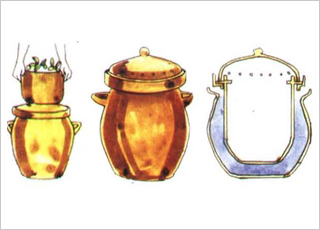
• Sheetal Matka in Rajasthan:
This is a traditional way of keeping fruits and vegetables fresh in Rajasthan – India.
There will be two clay pots kept one inside the other. Water will be kept in the outer pot and fruits and vegetables will be stored inside the inner pot. The water stored in the outer pot gets cooled and transfers coolness to the inner pot.
This is a traditional way of keeping fruits and vegetables fresh in Rajasthan – India.
There will be two clay pots kept one inside the other. Water will be kept in the outer pot and fruits and vegetables will be stored inside the inner pot. The water stored in the outer pot gets cooled and transfers coolness to the inner pot.


• Vegetable cooling in Africa:
Same way, Sheetal Matka is used in African countries to keep the vegetables cool and fresh, the difference is that they will fill the intermediate gap with sand and then pour water into it, which makes the pots cool and vegetables stored inside fresh.
(eg. Vegetable storage in African countries)
Same way, Sheetal Matka is used in African countries to keep the vegetables cool and fresh, the difference is that they will fill the intermediate gap with sand and then pour water into it, which makes the pots cool and vegetables stored inside fresh.
(eg. Vegetable storage in African countries)

• Water bags in Rajasthan (Davidi):
Water bags made of Canvas also known as Davidi were used in Rajasthan – India. These bags will keep the water cool and can easily be transported. The people who travel in deserts on camels and lorry driver use these bags.
Water bags made of Canvas also known as Davidi were used in Rajasthan – India. These bags will keep the water cool and can easily be transported. The people who travel in deserts on camels and lorry driver use these bags.

• Water purifying with sun rays:
In olden days water was purified with cloth filters and kept in the jars outside were the sun rays are available.
In olden days water was purified with cloth filters and kept in the jars outside were the sun rays are available.
• Climate control inside the rooms:
In Kerala, for controlling the temperature inside the rooms wooden ceiling (Thattu) were done, and usually people put mud over these ceiling. The roofs were made using coconut leaves or clay tiles locally called as Oodu.
• Water cooling:
For keeping the water cool inside the Matka people used to put local granite stones and use Ramacham and other Medicinal plants roots.
Water Cooling:
• Principle of water cooling:
The method or the principle of cooling water followed is Evaporative cooling.
Evaporative Cooling:
The basic principle relies on cooling by evaporation. When water evaporates it draws energy from the surroundings which produces a considerable cooling effect. Evaporative cooling occurs when air, which is not too humid, passes over a wet surface. The faster the rate of evaporation the greater the cooling will be. The efficiency of an evaporative cooler depends on the humidity of the surrounding air. Very dry air can absorb a lot of moisture so greater cooling occurs. In the extreme case of air, that is totally saturated with water, no evaporation can take place and no cooling occurs.
Generally, an evaporative cooler is made of a porous material that is fed with water. When hot dry air is drawn over the material, the water evaporates into the air raising its humidity and at the same time reducing the temperature of the air.
Assuming the earthenware pot absorbs some of the water in it (which it will, if it is not sealed with a glaze or other coating), the outside of the pot will be slightly moistened. As this moisture on the pot evaporates, the temperature of the pot is reduced due to evaporative cooling (same way sweat cools the body). This cooling effect will keep the temperature of the pot lower than it would otherwise be. This effect will only work as long as the outside of the pot is kept moist.
Water inside the bag:
Stage - 1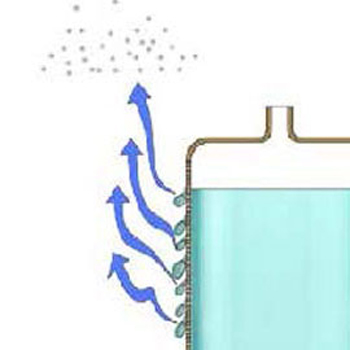

Stage - 2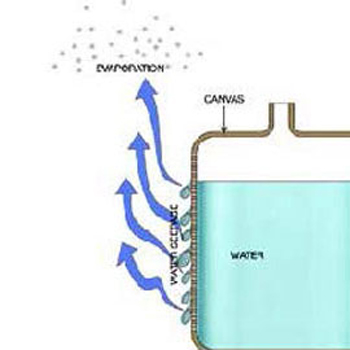

Stage - 3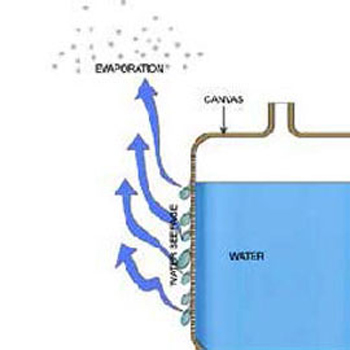

Stage - 4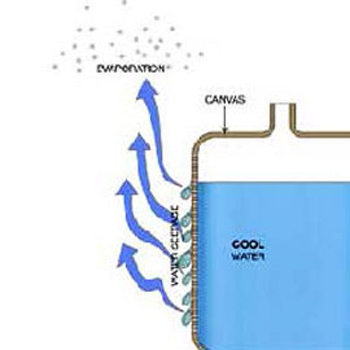

Stage - 5
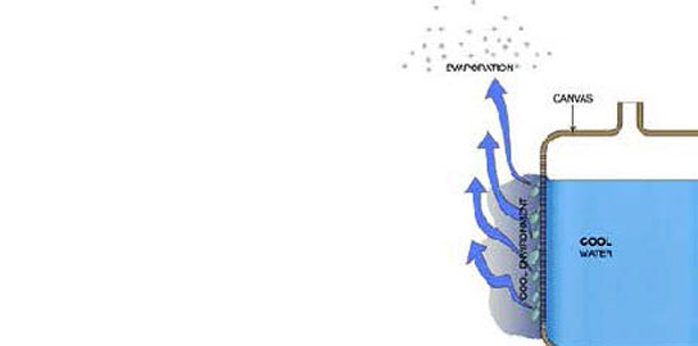
This is the basic principle of cooling water in Clay pots / Matka or Canvas/ Davidi.
Water containers:
There are different ways of carrying water, and different types of bags and containers are used all over the world. Some of the natural water containers that can cool water through evaporative cooling are as follows;
Matka or Clay pots

Gourd bottle

Bamboo bags

Canvas bags

Flax duck Canvas bag

Paper water bottle

Animal Skin water container
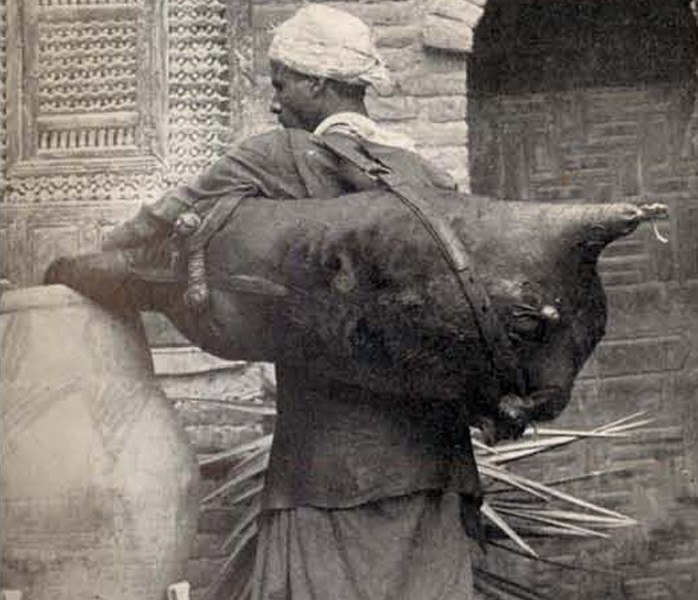

Following were some of the water bags which can store water
Military water bags -
These water bags are made of Polyester
These water bags are made of Polyester

Plastic water bags -
These water bags are made of Plastic
These water bags are made of Plastic


