

Just like Logic has an ordered arrangement of sentences or proposition, Narrative structure has an ordered arrangement of ‘Event’ sentences.
• A general Narrative structure has a following sequence of events:
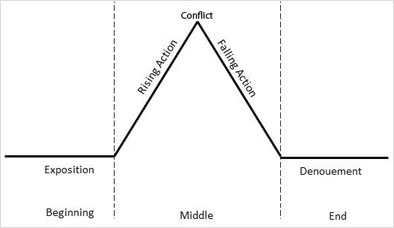
This structure has five general events:
Exposition, Rising action, Conflict, Falling Action and Denouement.
A variety of general sequence of events comes under this narrative structure.
- Exposition elaborates the current state of routine affairs.
- The Rising Action details some disturbance in the otherwise peaceful routine affairs.
- The rising action leads to a point of maximum Conflict.
- Then event that results in resolution (Falling Action) of conflict happens.
- This finally leads to the return of peaceful new state (Denouement)
These five narrative events can be mapped onto a scientific inquiry event. In the case of a scientific inquiry, the five events become:
- Exposition > Existing belief
- Rising Action > Doubt
- Conflict > Hypothesis [hypothesis conflicts with existing belief]
- Falling Action> Experimentation [if the experiment is successful, but that is not necessary]
- Denouement > Establishment of a new belief or theory
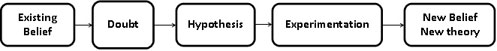
• It can also be graphically represented as:
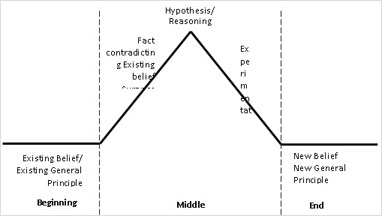
• Each event step can be described symbolically in the following manner:
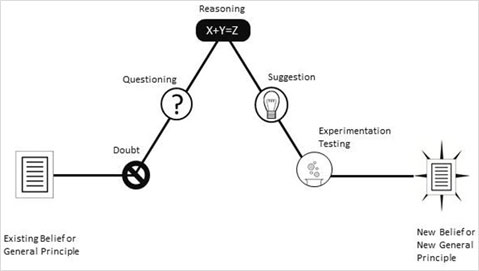
• The detailed narrative structure for a scientific inquiry event that leads to formulation and acceptance of a theory is given by:
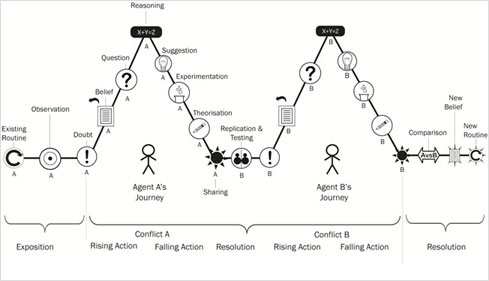
• Constituents of a scientific discovery event are:

• Description of each constituent element is given as follows:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Existing Belief or general principle is a sentence that describes relation between two or more concepts. |
 |
Existing routine is a sentence that describes a particular event that happens as expected according to Existing Belief. |
 |
Doubt is a sentence that describes a thought that occurs when a particular event does not happen according to some general principle. |
 |
Question is a Sentence that asks why particular event did not match general principle. |
 |
Reasoning is a sentence that searches for other similar events in the past and links them with current event. |
 |
Hypothesis/Suggestion is a statement that states a proposition regarding a new relation between concepts. |
 |
Experimentation is a sentence that states that one concept in the suggestion was present then the other concept was also found to be present as predicted. |
 |
Theory is a statement that states relation between certain concepts as a general principle or law. |
 |
Sharing with community is a sentence that describes an event or set of events in which the actor shares his/ her proposition of new belief with the community. |
 |
Replication is a sentence that describes an event or set of events in which the experiment done by an actor is repeated by another actor. |
 |
Comparison is a sentence in which the community debates about choosing the proposition to be accepted a s theory which will establish a new justified belief.is a sentence in which the community debates about choosing the proposition to be accepted a s theory which will establish a new justified belief. |